Straight Line Depreciation Formula, That Means, And Examples
Understanding straight line depreciation might help businesses and people handle their property extra effectively. Spreading expenses helps businesses manage budgets and plan for future wants. Additionally, straight line depreciation offers a clear image of an asset’s declining worth, which can be key to making knowledgeable selections about asset replacement or disposal.
This leads to an annual depreciation expense over the next 10 years of $7,000. Using the straight-line depreciation technique, the business finds the asset’s depreciable base is $40,000. Ending the formula, the business finds the asset’s annual depreciation amount is $4,000. The entire worth of the asset ($40,000 depreciable base) might be reclassified into the expense account over time.
Useful Life
Capitalized property are belongings that provide worth for multiple yr. Matching Precept in Accounting rules dictates that revenues and expenses are matched in the interval in which they’re incurred. Depreciation is a solution for this matching drawback for capitalized property as a result of it allocates a portion of the asset’s price in each year of the asset’s helpful life.
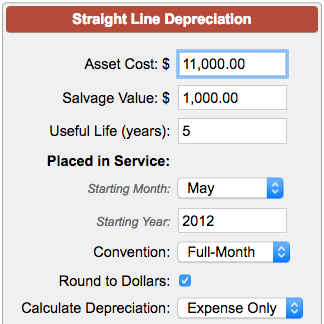
Depreciation Expense
Straight line method can additionally be convenient to use where no dependable estimate could be made regarding the sample of economic advantages expected to be derived over an asset’s helpful life. The methodology that takes an asset’s expected life and provides collectively the digits for annually is named the sum-of-the-years’-digits (SYD) technique. Determining monthly depreciation for an asset is dependent upon the asset’s useful life, in addition to which depreciation methodology you use.
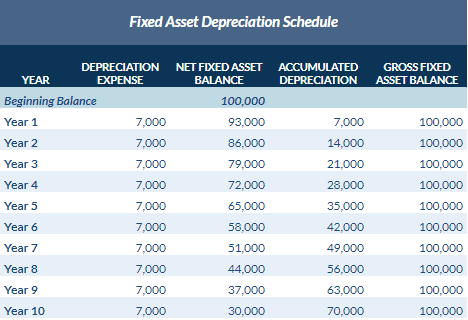
Regardless of the depreciation methodology used, the whole depreciation expense (and amassed depreciation) recognized over the life of any asset shall be equal. Nonetheless, the speed at which the depreciation is recognized over the life of the asset is dictated by the depreciation technique https://www.simple-accounting.org/ utilized. Unlike the other methods, the items of manufacturing depreciation method does not depreciate the asset based on time handed, however on the items the asset produced throughout the period.
An asset’s useful life is the length of time over which an organization expects the asset to continue to stay useful– to supply a profit to the business. It is the length of time over which an asset is depreciated because the expense from the asset should tie to the revenue generated by the asset in the identical period per the matching precept. Enter the total cost to acquire the asset, or the adjusted foundation, whichever is the lesser quantity (without dollar signal or any commas). If you would possibly be adjusting the depreciation schedule for over or under-reporting depreciation in prior years, enter the remaining depreciable base. After dividing the $1 million purchase value by the 20-year helpful life assumption, we arrive at $50k for the annual depreciation expense. In the straight line method of depreciation, the worth of the underlying fixed asset is reduced in equal installments each interval until reaching the tip of its helpful life.
- This is the difference between the acquisition value (adjusted basis) and the salvage value.
- Calculate straight line depreciation for the first, last, and interim years of an asset’s helpful life.
- Let’s contemplate a fictional business called “Tech Innovators Inc.” that recently bought a state-of-the-art laptop server for $20,000.
- Enter the name or description of the property if you’d like it included within the depreciation schedule.
To calculate using this method, first subtract the salvage worth from the original purchase value. Calculating the depreciating value of an asset over time can be tedious. Many accountants use a easy, easy-to-use methodology called the straight-line basis. This method spreads out the depreciation equally over each accounting period. Whereas the purchase value of an asset is thought, one should make assumptions relating to the salvage value and helpful life.
Understanding the professionals and cons might help you resolve if this depreciation method is correct for your corporation. This can result in errors on monetary statements by which assets could seem more priceless than they truly are. It Is essential to notice that the straight-line technique might not be appropriate if the asset’s utility considerably diminishes early on, or if it aligns extra closely with a usage-based depreciation mannequin. This expense reduces your net earnings, demonstrating how the depreciable asset contributes to your revenue era over time.
Excel stays one of the most practical instruments for managing depreciation schedules, especially for small to mid-sized companies. It’s accessible, versatile, and doesn’t require expensive software or steep learning curves. From small companies tracking a few laptops to manufacturing companies managing tens of millions in equipment, a depreciation schedule is essential for sustaining financial clarity and regulatory compliance. And one of the most common causes for a small business running out of working capital is the failure to set aside depreciation expenses as they accrue.

Advantages Of The Straight-line Method
This technique is helpful for businesses which have vital year-to-year fluctuations in manufacturing. Develop a depreciation schedule to visualize how property lose worth over time. This can help with budgeting, financial forecasting, and planning for replacements. Once you perceive the asset’s worth, it’s time to calculate depreciation expense utilizing the straight-line depreciation equation.
Your tree elimination enterprise is so successful that your wooden chipper will final for under 5 years before you need to exchange it (useful life). You imagine that after 5 years, you’ll have the flexibility to promote your wooden chipper for $3,000 (salvage value). Companies use straight-line depreciation in everyday eventualities to calculate the width of business assets.




Leave a comment